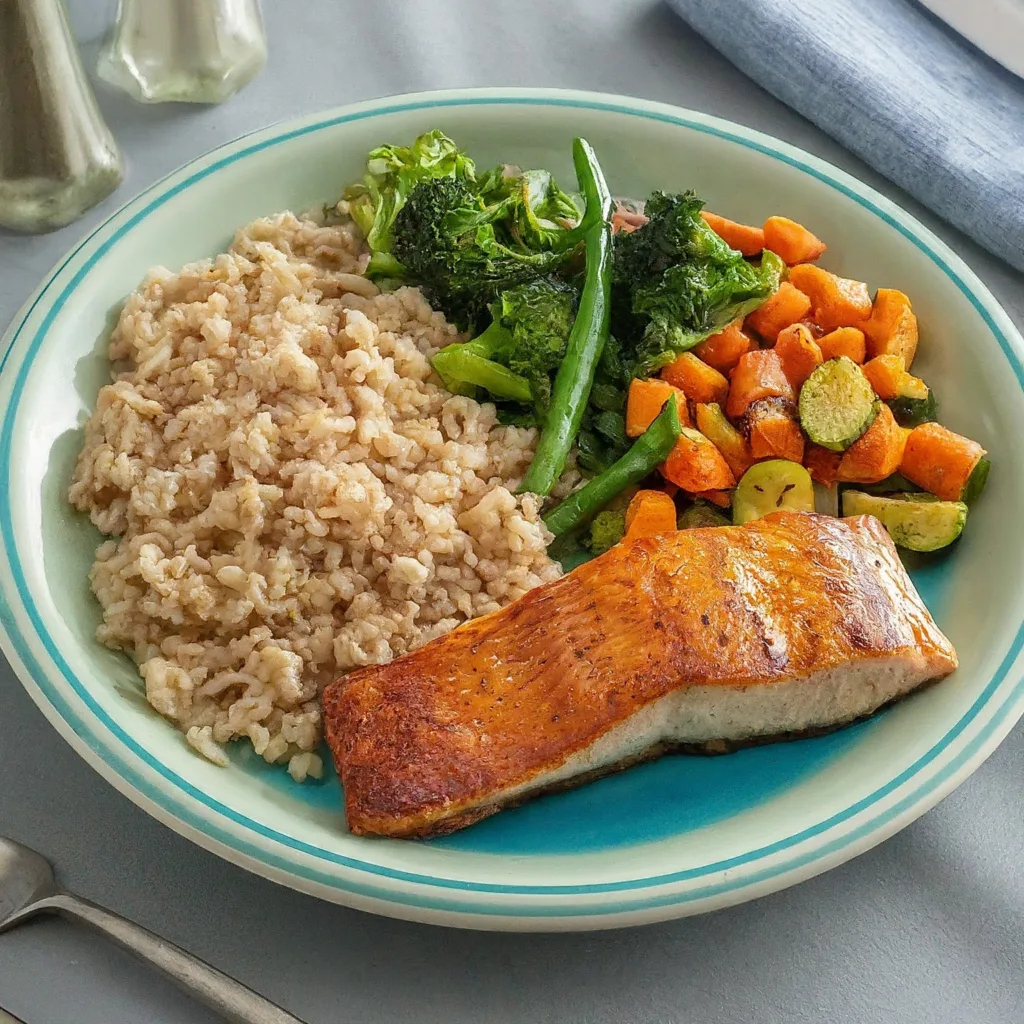The Japanese diet program includes whole foods based diet plans that will help you rapid weight loss in 7 days.
It is a complete diet rich in fish, seafood and plant-based foods, with a minimal amount of animal protein, sugar, and fat.
It is based on traditional Japanese cuisine, also known as “Washoku”, which includes small dishes of simple, refreshing and seasonal ingredients.
You are advised to drink water between meals to meet the requirement of 8 cups of water plan per day.
Japanese diet plan eating pattern is rich in nutrients and can provide many health benefits including weight loss, digestion, longevity and overall health.
This article explains you everything about the Japanese diets you need to know.
What is Japanese Diet
The Japanese diet consists of minimally processed, seasonal foods served in a variety of small dishes.
This style of eating emphasizes the natural flavors of the dishes rather than sauces or seasonings.
The Japanese diet is rich in boiled rice, noodles, fish, tofu, natto, seaweed, and fresh, cooked, or pickled fruits and vegetables, but is low in added sugars and fats. It may also include some eggs, dairy or meat, although these are usually a small part of the diet.
This contrasts with modern Japanese food, which has Western and Chinese influences and contains large amounts of animal protein and processed foods.
Japanese diet is known for its rich ummi taste, which is described as the fifth flavor – different from sweet, salty, sour, and bitter. Naturally occurring umami enhances the taste of foods rich in vegetables and other nutrients in Japanese cuisine. 1
Visual appeal is another important aspect of the Japanese diet. Dishes are eaten with chopsticks cut into small pieces, as this method is believed to create a rich harmony of flavors.
Hot green tea or cold barley tea are the drinks of choice, while beer and sake, alcoholic drinks are usually reserved for dinner. Snacks are uncommon and rarely eaten. 2
How to follow Japanese diet
Determine excess weight
To determine weight level, you need to know your BMI, which is the body mass index.
- Obesity: BMI is 30 or more.
- Pre-obesity: BMI 25 to 30.
- Overweight or Obesity: 25 or more have been described as overweight or obese.
There are many ways to measure fat levels based on a person’s fat level or weight and other physical observatory functions.
1. DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry)
DEXA was first invented to measure bone density, but the imaging function of this X-ray can determine the amount of fat in the human body.
This method involves using different mass of body fat, tissues, and also identifying which parts of the body contain more fat and contain the least amount of fat.
This is one of the modern tests to be considered true and correct for fat as the actual amount of fat will be seen through imaging obtained through X-rays.
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry requires a great deal of medical equipment that is expensive, and also requires professionals to operate the machine for accurate results.
2. Hydrostatic weighing
The second method for determining body fat is hydrostatic weight, and involves submerging (dipping) the body completely in water.
In submersion, a material is provided that will act in determining the body weight of a person in water. Submerged weight is compared with dry weight to determine the actual and definite overall body density of the individual. Muscle and fat levels are also considered, through which body fat is estimated.
This assessment is close to perfect in most circumstances. In addition, hydrostatic weighing require trained professionals for proper results.
3. Bioelectricalimpedance analysis
Using this method, the electrical resistance of the body is measured using the electric current passed through the body. It is important to know that muscle and fat conduct electricity differently, so it is easy to determine body fat percentage content.
Unlike the above methods of determining fat, “Bioelectricalimpedance analysis” process requires little training and can be used at home by amateurs to assess their body fat percentage.
However, factors such as body temperature and hydration can affect body mass index. Therefore, taking care is needed while performing this experiment.
4. Skin Folds Calipers or Pinch Test
This method involves pinching the skin at some point on the body and measuring the thickness of the field obtained.
This pattern of measurement focuses on the amount of fat directly under the skin. Therefore, after analysis, the actual body weight can be determined without much testing or measurement.
The measure also aims to determine body surface fat distribution. Even though fats not directly deposited under the skin may not be measured, further calculations will establish a closer estimate of the amount of fat available in the body.
5. Simple Weighing
In this case, your weight will be measured with a simple weight scale and calculated with the optimal required weight to determine whether your weight is optimal. Although this method is the least accurate, it is almost the most widely used worldwide.
For accurate measurement in determining overweight or obesity, factors such as muscle, body type, and height must be taken into consideration. For a start, you can use the scale, but if you doubt the result, you may need to apply more advanced methods.
6. Body Volume Index
This technique is the use of 3D software to determine the true image of a person. It functions and results based on the BVI rating, taking into account differences in the body mass index of the individual.
This method overcomes the obstacle of shape and various other functions or characteristics that is particular to individuals.
The software measure mainly where fat is located and does not need to calculate the total weight. The abdomen is not the only condition whose weight is determined, so the BVI system is considered more body parts.
Japanese diet fact need to know
Considering the importance of optimal body weight, there are diet facts that you need to be aware of to lose weight without the need for rigorous exercise and other unhealthy methods or weight loss approaches.
1. Drink water
Being dehydrated is not a good option and supplementing water when necessary should be done when consuming less fat. In addition, you should resort to non-alcoholic beverages, and natural fruits and fruit juices when needed. 6 to 8 glasses of water are needed to aid digestion for optimal fluid flow. This is more important when the weather is warm; You can have four glasses and get optimal digestion when the weather is cool.
2. Do exercise
Despite the effort to keep rigorous exercise at bay, staying active is very important for achieving proper health. A balanced diet is not enough to achieve good health and weight. To avoid the risk of developing stroke, heart disease, cancer or type-2 diabetes, it is important that you do simple exercises to keep your body running. Toxins and wastes are easily roasted, and you will achieve optimal health in the end.
3. Low amount of salt
Your sugar and salt intake should be balanced. To reduce the risk of high blood pressure, you need to consume a particular amount of salt on a daily basis. Use the information on the food label to determine the amount of salt in a given food item.
A food item containing 1.5 per 100 grams suggests that it has a high salt content. For good health, you should not take more than 6g salt daily.
In addition, salt levels in the body can be controlled through simple exercises such as walking in the morning or evening.
4. Carefull with sugar
Even though sugar may have high energy, excess consumption contributes to lower body and body weight gain in general. Sugar can also cause tooth decay due to other diseases.
You should pay attention to the things you consume that contain more sugar than your body. Buy fruit juices, syrups, and natural honey friendly to reduce your sugar intake.
Do not take a soda bottle if not necessary. To reduce the need for soft drinks, always consume more water and eat enough food, which contains the most sugars every day. Pastries, biscuits, cakes, processed cereals, alcoholic beverages and sugary fizzy beverages should be avoided as much as possible.
5. Do not eat saturated fat
Saturated fat can increase the amount of cholesterol in the blood and therefore increase the risk of developing heart disease.
On average, you should not have more than 30 grams of saturated fat on a daily basis. Women, in particular, should not have more than just 20 grams of saturated fat.
Look for foods such as pies, lard, butter, cream, sausage, biscuits, cakes and hard cheese. These foods contain a significant amount of saturated fat which should be avoided as much as possible.
Foods with unsaturated fats include avocados, oily fish and vegetable oils.
6. Eat fish
Fish contains vitamins and minerals, and is an excellent source of protein.
Asians consume fish every day, so their lives are healthy. Fish contains omega-3 fatty acids that help prevent heart disease. This oily fish includes pilchards, sardines, fresh tuna, herring, trout, mackerel, and salmon.
Non-oily fish include hake, Skake, canned tuna, cod, Coley, and haddock. It is always important to select a wide variety of fish to ascertain the range of health benefits of fish consumption.
Foods to eat in Japanese diet
The Japanese diet is rich in the following foods:
- Seafood and Fish: All types of seafood and fish can be included. These can be boiled, baked, grilled or raw – as is the case with sushi and sashimi.
- Soy foods: The most common are edamame, tofu, miso, soy sauce, tamari, and nato.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Typically, fruits are eaten raw or as pickles, while vegetables are steamed, sautéed, pickled, boiled in broth or added to soups.
- Seaweed: Sea vegetables are a large part of the Japanese diet. They are usually eaten raw or dried.
- Tempura: This light flour is made by mixing wheat flour with iced or sparkling water. It serves as a batter for deep-fried vegetables and seafood.
- Rice or Noodles: Steamed rice is a staple in a Japanese diet. Other popular options include soba, ramen, or udon noodles which are served in a cold or hot broth.
- Drinkable items: Hot black or green tea and cold barley tea are the main beverages, although beer and sake can be served with dinner.
How to add food in Japanese meal
Japanese food usually consists of a soup, a main dish and side dishes combined with some sides.
- Main food: boiled rice or soba, ramen or udon noodles
- Soup: Usually a faux soup made with seaweed, shellfish, or tofu and vegetables in fermented soybean stock – although vegetable or noodle soups are other popular choices.
- Main dish: fish, seafood, tofu with optional small amounts of meat, chicken or eggs
- Side dishes: Vegetables (raw, boiled, boiled, fennel, grilled or pickled), wild plants, seaweed, and raw or pickled fruits
Sample-1 of 7 days Japanese diet meal plan
Day 1 meal plan
| Breakfast | Black or Green tea |
| Lunch | Olive oil; Romaine lettuce salad; 8 oz. of broiled beef steak; 2 hard-boiled eggs. |
| Dinner | 8 oz. beef steak Any fruits |
Day 2 meal plan
| Breakfast | Black coffee |
| Lunch | Olive sucked with romaine salad lettuce sliced fresh carrot; 3 hard-boiled eggs; Lemon juice should be included. |
| Dinner | Olive with lettuce salad, romaine in particular; 15 oz. broiled or steamed chicken breast. |
Day 3 meal plan
| Breakfast | 2 carrots; Dressed with lemon juice; (Fresh carrots are preferable where available). |
| Lunch | Olive oil with romaine salad; 7 oz. of broiled beef steak; 3 hard boiled eggs. |
| Dinner | 2 cups unsalted tomato; 17 oz. Large boiled, steamed or broiled fish. |
Day 4 meal plan
| Breakfast | Green tea |
| Lunch | 6 oz. Broiled beef steakn; Olive oil, with romaine lettuce salad; 3 hard-boiled eggs. |
| Dinner | Fry one large root of fennel or parsnip; Consume with apples. |
Day 5 meal plan
| Breakfast | Black coffee |
| Lunch | 3 large fresh carrots; 1 hard boiled egg. |
| Dinner | Dress boiled carrots with lemon juice; Olive oil (oil should be included in the boiling process). |
Day 6 meal plan
| Breakfast | 1 toast; Black coffee. |
| Lunch | Romaine lettuce salad (with olive oil); Boiled, steamed or broiled fish. |
| Dinner | 7 oz. Grilled beef steak; 1 low-fat plain yoghurt |
Day 7 meal plan
| Breakfast | Tea or Black coffee |
| Lunch | Boiled, steamed or broiled fish; Add a fresh tomato to an olive oil romaine lettuce. |
| Dinner | Tea or Black coffee |
Sample-2 of 7 days Japanese diet meal plan
Here is a sample-2 7-day Japanese diet plan that incorporates some of the key elements of the traditional Japanese diet:
Day 1:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of grilled fish (4 oz.) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: Sushi or sashimi (4 oz. raw fish or seafood) with a side of miso soup (1 cup)
- Dinner: A bowl of udon noodles (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz.)
Day 2:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of poached eggs (2) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: A salad made with mixed greens (2 cups), fish (4 oz.), and tofu (4 oz.)
- Dinner: A bowl of ramen (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz.)
Day 3:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of grilled fish (4 oz.) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: A bento box with a variety of traditional Japanese foods, including sushi (2 pieces), sashimi (4 oz.), tempura (2 pieces) and pickled vegetables (1/4 cup)
- Dinner: A bowl of soba noodles (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz.)
Day 4:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of poached eggs (2) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: A salad made with mixed greens (2 cups), fish (4 oz.), and tofu (4 oz.)
- Dinner: A bowl of ramen (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz.)
Day 5:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of grilled fish (4 oz.) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: A bento box with a variety of traditional Japanese foods, including sushi (2 pieces), sashimi (4 oz.), tempura (2 pieces) and pickled vegetables (1/4 cup)
- Dinner: A bowl of soba noodles (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz.)
Day 6:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of poached eggs (2) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: A salad made with mixed greens (2 cups), fish (4 oz.), and tofu (4 oz.)
- Dinner: A bowl of ramen (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz.)
Day 7:
- Breakfast: A bowl of steamed brown rice with a side of grilled fish (4 oz.) and mixed vegetables (1 cup)
- Lunch: Sushi or sashimi (4 oz. raw fish or seafood) with a side of miso soup (1 cup)
- Dinner: A bowl of udon noodles (1 cup) with a variety of vegetables (1 cup) and seafood (4 oz)
These 7-day diet plan for weight loss based on the traditional Japanese diet would likely include a focus on lean protein sources, such as fish and seafood, as well as plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. It would also limit processed foods and added sugars.
This Japanese diet plan is just a sample, and you can always adjust it to your needs and preferences. These 7-day diet plan that incorporates above principles, but please note that it’s important to consult a doctor or a nutritionist before making any big changes. Additionally, it’s essential to make sure that the diet plan is tailored to your specific needs, preferences and dietary restrictions if any.
It’s influential to note that, like any diet, it’s essential to consult a doctor or a nutritionist before making any big changes.
Health Benefits of Japanese Diet
The Japanese diet is rich in nutrients and can aid digestion, weight loss, and longevity. This diet can also reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
The Japanese diet is associated with an array of health benefits.
1. Nutrient-rich and beneficial compounds
- Japanese diet is naturally rich in fiber, calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron and various nutrients including vitamins A, C, and E. 3
- There is also a good amount of seaweed and green tea in the diet. Both are great sources of antioxidants, which are beneficial compounds that protect your body from cellular damage and disease. 4
- Vegetables contribute to the nutrient density of this diet and are often cooked in Dashi, a dried fish and seafood, vegetable based stock. This reduces their quantity and enhances their taste, making it easier to eat large amounts.
- What’s more, many fish- and seaweed-based dishes included in this diet have long been providing omega-3 fats, which promote brain, eye, and heart health. 5
2. It can prevent chronic diseases
- The Japanese diet can protect against conditions such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
- It is naturally rich in fish and seafood, seaweed, green tea, soy, fruits, and vegetables, but is low in added sugar, fat, and animal protein – all factors protecting against heart disease.
- In fact, the risk of heart disease in Japanese people is unexpectedly low despite their high salt intake, which usually increases the risk of heart disease. 6
- What’s more, in a 6-week study of 33 men following a Japanese diet, 91% experienced significant reductions in risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including excess weight and high LDL (poor) cholesterol levels. 78
- In addition, high green tea intake encouraged on this diet can prevent Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and some types of cancer. 9 10 11 12
3. It can help you live longer
- Japan has the highest life expectancy in the world, which many experts attribute to the Japanese diet. 13 14 15 16
- In fact, the Japanese island of Okinawa is considered a blue zone, an area with much greater longevity. Keep in mind that the Okinawa diet focuses too much on sweet potato and contains less rice and fish than the Japanese diet.
- In a 15-year study on more than 75,000 Japanese people, those closely following the Japanese diet experienced a 15% lower risk of premature death than Western diet eaters. 2
- Experts emphasized the Japanese diet as a whole, minimally processed foods by increasing it, as well as its low fat and sugary foods. 1
Exercise Schedule and Cookbook
Note that you are about to combine this dietary formula with a planned exercise workout to achieve maximum results.
- Circuit training
- Full yoga sequence
- Bodyweight circuit workout
- Exercise Routine for men and women
- Abs shaping workouts
- Workouts for love handles
- Yoga for belly fat
- Workout routine for legs
If you want to know more about the traditional Japanese diet, you can find many books on this subject. While browsing, look for books that focus on whole foods and do not offer Western cuisine/recipes.
- Japanese Cookbook for Beginners
- Japanese home cooking
- Traditional Japanese cuisine book
- Complete Japanese cook book for slimming
- Gabriel AS, Ninomiya K, Uneyama H. “The Role of the Japanese Traditional Diet in Healthy and Sustainable Dietary Patterns around the World.” Nutrients. 2018 Feb 3;10(2):173. doi: 10.3390/nu10020173. PMID: 29401650; PMCID: PMC5852749.[↩][↩]
- Kurotani K, Akter S, Kashino I, Goto A, Mizoue T, Noda M, Sasazuki S, Sawada N, Tsugane S; Japan Public Health Center based Prospective Study Group. “Quality of diet and mortality among Japanese men and women: Japan Public Health Center based prospective study.” BMJ. 2016 Mar 22;352:i1209. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1209. PMID: 27005903; PMCID: PMC4804125.[↩][↩]
- Tomata Y, Zhang S, Kaiho Y, Tanji F, Sugawara Y, Tsuji I. “Nutritional characteristics of the Japanese diet: A cross-sectional study of the correlation between Japanese Diet Index and nutrient intake among community-based elderly Japanese.” Nutrition. 2019 Jan;57:115-121. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jul 11. PMID: 30157468.[↩]
- Pem D, Jeewon R. “Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Benefits and Progress of Nutrition Education Interventions- Narrative Review Article.” Iran J Public Health. 2015 Oct;44(10):1309-21. PMID: 26576343; PMCID: PMC4644575. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4644575.[↩]
- Calder PC. “Very long-chain n-3 fatty acids and human health: fact, fiction and the future.” Proc Nutr Soc. 2018 Feb;77(1):52-72. doi: 10.1017/S0029665117003950. Epub 2017 Oct 17. PMID: 29039280.[↩]
- Shimazu T, Kuriyama S, Hozawa A, Ohmori K, Sato Y, Nakaya N, Nishino Y, Tsubono Y, Tsuji I. “Dietary patterns and cardiovascular disease mortality in Japan: a prospective cohort study.” Int J Epidemiol. 2007 Jun;36(3):600-9. doi: 10.1093/ije/dym005. Epub 2007 Feb 22. PMID: 17317693.[↩]
- Maruyama C, Nakano R, Shima M, Mae A, Shijo Y, Nakamura E, Okabe Y, Park S, Kameyama N, Hirai S, Nakanishi M, Uchida K, Nishiyama H. “Effects of a Japan Diet Intake Program on Metabolic Parameters in Middle-Aged Men.” J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017 Apr 3;24(4):393-401. doi: 10.5551/jat.36780. Epub 2016 Sep 21. PMID: 27667329; PMCID: PMC5392477.[↩]
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/risk-factors-type-2-diabetes[↩]
- Mandel SA, Amit T, Weinreb O, Reznichenko L, Youdim MB. “Simultaneous manipulation of multiple brain targets by green tea catechins: a potential neuroprotective strategy for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases.” CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):352-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00060.x. PMID: 19040558; PMCID: PMC6493995.[↩]
- Ogunleye AA, Xue F, Michels KB. “Green tea consumption and breast cancer risk or recurrence: a meta-analysis.” Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Jan;119(2):477-84. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0415-0. Epub 2009 May 13. PMID: 19437116.[↩]
- Kurahashi N, Sasazuki S, Iwasaki M, Inoue M, Tsugane S; JPHC Study Group. “Green tea consumption and prostate cancer risk in Japanese men: a prospective study.” Am J Epidemiol. 2008 Jan 1;167(1):71-7. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwm249. Epub 2007 Sep 29. PMID: 17906295.[↩]
- Chen Y, Wu Y, Du M, Chu H, Zhu L, Tong N, Zhang Z, Wang M, Gu D, Chen J. “An inverse association between tea consumption and colorectal cancer risk.” Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(23):37367-37376. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16959. PMID: 28454102; PMCID: PMC5514915.[↩]
- Willcox DC, Willcox BJ, Hsueh WC, Suzuki M. “Genetic determinants of exceptional human longevity: insights from the Okinawa Centenarian Study.” Age (Dordr). 2006 Dec;28(4):313-32. doi: 10.1007/s11357-006-9020-x. Epub 2006 Dec 8. PMID: 22253498; PMCID: PMC3259160.[↩]
- Willcox DC, Willcox BJ, He Q, Wang NC, Suzuki M. “They really are that old: a validation study of centenarian prevalence in Okinawa.” J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008 Apr;63(4):338-49. doi: 10.1093/gerona/63.4.338. PMID: 18426957.[↩]
- Ikeda N, Saito E, Kondo N, Inoue M, Ikeda S, Satoh T, Wada K, Stickley A, Katanoda K, Mizoue T, Noda M, Iso H, Fujino Y, Sobue T, Tsugane S, Naghavi M, Ezzati M, Shibuya K. “What has made the population of Japan healthy?” Lancet. 2011 Sep 17;378(9796):1094-105. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61055-6. Epub 2011 Aug 30. PMID: 21885105.[↩]
- Kurotani K, Akter S, Kashino I, Goto A, Mizoue T, Noda M, Sasazuki S, Sawada N, Tsugane S; Japan Public Health Center based Prospective Study Group. “Quality of diet and mortality among Japanese men and women: Japan Public Health Center based prospective study.” BMJ. 2016 Mar 22;352:i1209. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1209. PMID: 27005903; PMCID: PMC4804125.[↩]