“10 Crucial Diet Mistakes Aging Faster” are more than simply minor dietary errors; they are catalysts that accelerate the aging process. In order to maintain a youthful appearance and vitality, recognizing and rectifying dietary errors is paramount.
Contrary to common misconceptions, aging isn’t solely dictated by genetics or skincare routines. The foods we consume play a major effect in shaping our overall well-being and how quickly we age.
By identifying and correcting these dietary pitfalls, we can effectively slow down the aging process and preserve our youthful skin glow.
In This “Crucial Diet Mistakes Aging Faster”
Top 10 Crucial Diet Mistakes Aging Faster
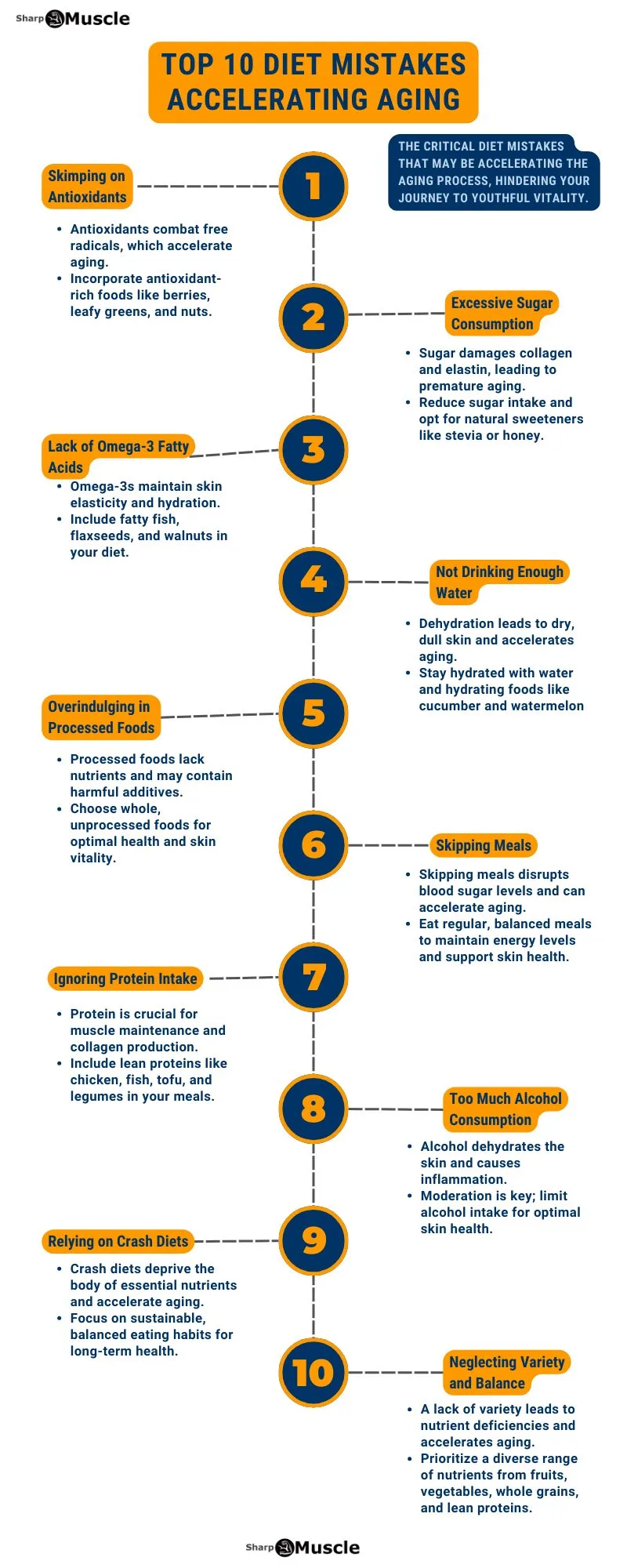
The “10 Crucial Diet Mistakes Aging Faster” uncover actionable insights to optimize your diet for anti-aging benefits. From skimping on antioxidants to neglecting variety and balance, these dietary blunders may be undermining your efforts to maintain a youthful appearance and vitality.
Let’s delve into each of these mistakes and learn how to make healthier choices to support optimal aging and overall health.
1. Skimping on Antioxidants
Skimping on antioxidants can have detrimental effects on overall health and accelerate the aging process. 1
Individuals who consistently consume diets low in antioxidant-rich foods may experience increased oxidative stress in their bodies. This oxidative stress can lead to cellular damage and inflammation, which are key factors in premature aging and the development of age-related diseases such as 2:
Additionally, insufficient intake of antioxidants may impair the body’s ability to repair and regenerate cells, further contributing to premature aging signs such as wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
So antioxidants play a crucial role in combating free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the aging process. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help to protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation, thereby supporting overall health and longevity.
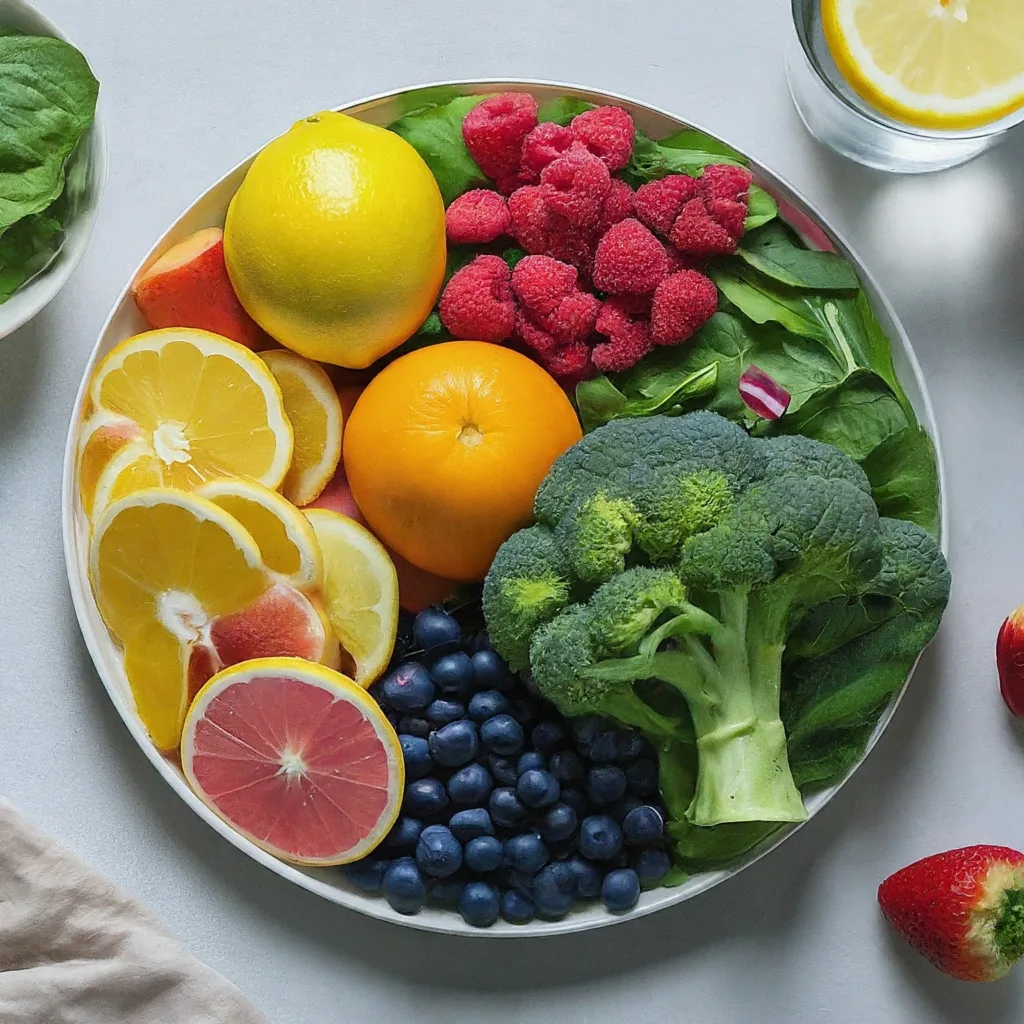
Incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into the diet is an excellent way to boost your intake of these beneficial compounds. Some examples of antioxidant-rich foods include:
- berries (such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries)
- dark leafy greens (like spinach and kale)
- nuts and seeds, colorful vegetables (such as bell peppers and carrots)
- certain spices (like turmeric and cinnamon).
By including these foods in your youthful skin diet regularly, you can help to counteract the effects of aging process and promote optimal health.
2. Excessive Sugar Consumption
The harmful effects of sugar on collagen and elastin can accelerate the aging process by causing glycation, a process where sugar molecules bind to proteins in the skin, resulting in the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs). 4 5
This can lead to a loss of elasticity and firmness in the skin, contributing to premature aging and the development of wrinkles.
Reducing sugar intake is crucial for maintaining youthful skin and overall health. One tip for reducing sugar intake is to opt for natural sweeteners such as:
- stevia,
- monk fruit,
- erythritol instead of refined sugars.
These alternatives can satisfy sweet cravings without causing spikes in blood sugar levels.
Additionally, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods can help reduce sugar consumption, as many processed foods and beverages contain hidden sugars. Choosing fresh fruits as a healthier alternative to sugary snacks and desserts can also help satisfy sweet cravings while providing beneficial nutrients and antioxidants for the skin.
Incorporating more fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, legumes, and whole grains into your diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings for sugary foods. Consuming healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, and seeds can also help keep you feeling satisfied and curb cravings.
By making these simple dietary changes and being mindful of your sugar intake, you can support your skin’s health and slow down the aging process, helping you maintain a youthful skin appearance for years to come.
3. Lack of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The lack of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet can contribute to age faster and a variety of health issues.
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are essential nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining overall health, including cardiovascular health, brain function, and inflammation regulation. 6
When the diet lacks sufficient omega-3 fatty acids, it can lead to various health problems, including increased inflammation, decreased cognitive function, and impaired cardiovascular health. In terms of aging process, the deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids can result in decreased skin elasticity and hydration, leading to premature aging signs such as wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity and hydration by supporting the skin’s lipid barrier function. This barrier helps to lock in moisture and protect the skin from environmental damage, keeping it supple and hydrated.
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are highly beneficial for skin health. Consuming these fish regularly can help improve skin texture and reduce dryness and inflammation.
For those following a plant-based diet, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds are rich sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid that can be converted into EPA and DHA in the body. Adding these seeds to your meals or incorporating them into smoothies and salads is a convenient way to boost your omega-3 intake.
Walnuts are another excellent source of ALA and provide additional nutrients such as vitamin E and antioxidants, which further support skin health. 7
Snacking on a handful of walnuts or adding them to oatmeal, yogurt, or baked goods can help increase your omega-3 intake and promote healthy, radiant skin.
Incorporating these omega-3-rich foods into your diet regularly can help maintain skin elasticity, improve hydration, and protect against premature aging, ensuring that your skin remains youthful and glowing for years to come.
4. Not Drinking Enough Water
Dehydration can accelerate the aging process by causing dryness and dullness in the skin. 8
When the body is dehydrated, the skin lacks moisture, leading to a loss of elasticity and firmness. This can exacerbate the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, making the skin look older and more tired.
Additionally, dehydration can impair the skin’s ability to function as a barrier, making it more susceptible to damage from environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollutants. This can further accelerate the aging process and lead to premature aging signs such as sunspots, uneven skin tone, and rough texture.
To combat dehydration and maintain youthful-looking skin, it’s essential to stay hydrated throughout the day. Recommendations for staying hydrated include drinking an adequate amount of water daily, typically around 8 glasses or more depending on individual needs and activity levels.
In addition to plain water, consuming hydrating foods such as fruits and vegetables can also contribute to overall hydration. Including foods with high water content in your youthful skin diet can help replenish fluids and electrolytes lost through sweat and exertion.
The high water foods include:
- cucumber,
- watermelon,
- strawberries,
- oranges.
Moreover, limiting the intake of dehydrating beverages such as alcohol and caffeinated drinks can help prevent dehydration. These beverages have diuretic effects, which can increase fluid loss and exacerbate dehydration.
Incorporating a combination of water intake, hydrating foods, and avoiding dehydrating beverages, in your anti-aging nutrition plan, can help maintain optimal hydration levels and support healthy, youthful-looking skin for years to come.
5. Overindulging in Processed Foods
Processed foods often lack essential nutrients and may contain harmful additives that can accelerate the aging process. 9 10
These foods are typically high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, while being low in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Consuming processed foods regularly can lead to nutrient deficiencies and contribute to various health issues, including premature aging.
To counteract the effects of processed foods on aging, it’s essential to focus on incorporating whole, minimally processed foods into the diet. Whole foods are nutrient-dense and provide a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are essential for maintaining youthful skin and overall health.
Some suggestions for healthier alternatives to processed foods include:
- Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley instead of refined grains like white rice and white bread.
- Opt for lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and lentils instead of processed meats like sausages and deli meats.
- Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables into your meals and snacks. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Use healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds in cooking and meal preparation instead of hydrogenated oils and trans fats found in many processed foods.
- Limit your intake of processed snacks, desserts, and beverages high in added sugars, artificial sweeteners, and preservatives. Instead, choose natural snacks like nuts, seeds, yogurt, and fresh fruit.
By focusing on whole foods and minimizing processed foods in your youthful skin diet scheme, or anti-aging nutrition plan, you can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to support healthy aging and maintain youthful vitality.
6. Skipping Meals
Skipping meals can lead to blood sugar imbalances, which can have detrimental effects on both your energy levels and your overall health. 11
When you skip meals, your body’s blood sugar levels can drop, leading to feelings of fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Over time, this can also contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of chronic diseases.
To avoid these negative consequences and support healthy aging, it’s important to prioritize balanced meals and snacks throughout the day. Here are some tips for creating balanced anti-aging nutrition meals and snacks to maintain steady energy levels:
- Include a combination of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats in each meal. Protein helps to stabilize blood sugar levels, while carbohydrates provide energy, and healthy fats help to keep you feeling satisfied.
- Choose complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which are rich in fiber and release energy slowly, helping to maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and lentils into your meals to help keep you feeling full and satisfied.
- Include healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil to provide long-lasting energy and support brain health.
- Don’t forget to hydrate! Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help prevent dehydration and support optimal energy levels.
- Plan ahead and pack healthy snacks to have on hand when hunger strikes between meals. Choose nutrient-dense options such as nuts, seeds, yogurt, fruit, and vegetables with hummus or nut butter.
By prioritizing balanced meals and snacks and avoiding skipping meals, you can help maintain steady blood sugar levels, support healthy energy levels, and promote overall well-being and longevity.
7. Ignoring Protein Intake
Ignoring protein intake can have significant implications for overall health and aging. 12 13
Protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass, supporting immune function, and promoting collagen production, all of which are critical for healthy aging.
Muscle mass naturally declines with age, but adequate protein intake can help slow aging process by supporting muscle repair and growth. Maintaining muscle mass is crucial for mobility, strength, and independence as we age, reducing the risk of falls and frailty.
Additionally, protein plays a vital role in collagen production, the protein responsible for skin elasticity and firmness. Collagen production naturally declines with aging process, leading to wrinkles, sagging skin, and a loss of volume. By consuming adequate protein, you can support collagen synthesis and promote youthful-looking skin.
Examples of protein-rich foods to include in meals and snacks:
- Lean meats such as chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef or pork.
- Fish and seafood, particularly fatty fish like salmon, trout, and sardines.
- Eggs, which are a complete source of protein and contain essential amino acids.
- Plant-based sources of protein such as tofu, tempeh, lentils, beans, and chickpeas.
- Dairy products such as Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and cheese, which are also rich in calcium for bone health.
Incorporating these protein-rich foods into your anti-aging nutrition meals and snacks can help ensure you meet your daily protein needs and support muscle mass, collagen production, and overall health as you age.
8. Too Much Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on skin health and accelerate the aging process. 14 15
Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it increases urine production and can lead to dehydration. Dehydrated skin appears dry, dull, and less elastic, making fine lines and wrinkles more pronounced.
Moreover, alcohol can cause inflammation throughout the body, including the skin. Chronic inflammation can exacerbate skin conditions such as acne, rosacea, and eczema, and contribute to premature aging.
To moderate alcohol intake and support optimal skin health, consider the following strategies:
- Set limits: Establish a maximum number of drinks per day or week and stick to it. Be mindful of standard drink sizes and opt for lower-alcohol options when possible.
- Stay hydrated: Alternate alcoholic beverages with water or other hydrating drinks to help counteract the dehydrating effects of alcohol. Drinking water before, during, and after consuming alcohol can also help maintain hydration levels and support skin health.
- Choose quality over quantity: Opt for high-quality alcoholic beverages and savor them slowly, rather than consuming large quantities of low-quality drinks. Choose drinks with fewer additives and artificial ingredients, which can contribute to inflammation and skin irritation.
- Eat before drinking: Consuming a balanced meal before drinking alcohol can help slow down its absorption into the bloodstream and reduce its effects on the skin and overall health.
- Practice moderation: Be mindful of your alcohol consumption and its effects on your body and youthful skin. Listen to your body’s cues and know when it’s time to stop or slow down.
By implementing these strategies and moderating alcohol intake, you can support optimal skin health, reduce inflammation, and slow down the aging process, helping you maintain a youthful appearance and overall well-being.
9. Relying on Crash Diets
Crash diets, characterized by extreme calorie restriction and rapid weight loss, can deprive the body of essential nutrients and have detrimental effects on overall health, including accelerating the aging process. 16 17
These diets often lack essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients needed for proper bodily function and can lead to nutrient deficiencies, weakened immune function, and fatigue.
Additionally, crash diets can cause metabolic imbalances, including fluctuations in blood sugar levels and hormone levels, which can contribute to increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. Over time, this can accelerate the aging process and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
To adopt sustainable, balanced eating habits for long-term health and vitality, consider the following suggestions:
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods: Choose whole, minimally processed foods that are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats in your diet to ensure you’re getting a wide variety of nutrients to support overall health.
- Eat regularly: Instead of skipping meals or severely restricting calories, aim to eat balanced meals and snacks throughout the day to keep your energy levels stable and prevent nutrient deficiencies. Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues and eat when you’re hungry, stopping when you’re satisfied.
- Practice portion control: Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and bowls to help control portion sizes and prevent overindulgence.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support optimal bodily function. Limit sugary beverages and alcohol, which can contribute to dehydration and inflammation.
- Practice mindful eating: Slow down and savor your meals, paying attention to the taste, texture, and aroma of each bite. Avoid distractions such as screens or multitasking while eating, which can lead to mindless eating and overconsumption.
By adopting sustainable, balanced eating habits that prioritize nutrient-dense foods and regular meals, you can support long-term health, vitality, and slow down the aging process, ensuring you look and feel your best for years to come.
10. Neglecting Variety and Balance
Neglecting variety and balance in your diet can have significant consequences for overall health and vitality. 18 19
Consuming a diverse range of nutrients is essential for supporting bodily functions, maintaining energy levels, and promoting optimal health. By focusing on variety and balance in your anti-aging nutrition meals, you can ensure that you’re getting all the essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients your body needs to thrive.
Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your youthful skin diet is key to achieving balance and meeting your nutritional needs.
Here are some tips for creating balanced meals that incorporate a diverse range of nutrients:
- Aim for a rainbow of colors: Include fruits and vegetables of different colors in your meals to ensure you’re getting a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim to fill half your plate with colorful fruits and vegetables at each meal.
- Prioritize whole grains: Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley over refined grains like white rice and white bread. Whole grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals and can help keep you feeling full and satisfied.
- Include lean proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and lentils into your meals to support muscle growth and repair. Aim to include protein with each meal to help keep you feeling full and satisfied.
- Don’t forget healthy fats: Include sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in your meals to support heart health and brain function. These fats are essential for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins and promoting satiety.
- Mix it up: Experiment with different ingredients, flavors, and cuisines to keep your meals interesting and enjoyable. Try new fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins to add variety to your diet and prevent boredom.
By prioritizing variety and balance in your meals and snacks, you can ensure that you’re getting all the essential nutrients your body needs to support overall health and vitality. Incorporating a diverse range of foods into your diet can help prevent nutrient deficiencies, prevent aging process, support optimal energy levels, and promote long-term health and well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, the 10 crucial diet mistakes that can accelerate the aging process include:
- Skimping on antioxidants
- Excessive sugar consumption
- Lack of omega-3 fatty acids
- Not drinking enough water
- Overindulging in processed foods
- Skipping meals
- Ignoring protein intake
- Too much alcohol consumption
- Relying on crash diets
- Neglecting variety and balance
However, it’s never too late to make positive changes to improve your dietary habits and support overall well-being for a youthful appearance and increased longevity. By making small, sustainable changes to your diet, such as incorporating more antioxidant-rich foods, reducing sugar intake, and prioritizing hydration, you can support healthy aging and promote optimal skin health.
Additionally, focusing on balanced meals that include a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide your body with the essential nutrients it needs to thrive. Remember that consistency is key, and even small changes can have a significant impact on your health and well-being over time.
By taking proactive steps to improve your dietary habits and prioritize your health, you can look and feel your best at any age. Embrace the journey towards better nutrition and enjoy the benefits of a healthier, more vibrant life.
- Warraich UE, Hussain F, Kayani HUR. “Aging – Oxidative stress, antioxidants and computational modeling.” Heliyon. 2020 May 31;6(5):e04107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04107. PMID: 32509998; PMCID: PMC7264715.[↩]
- Pham-Huy LA, He H, Pham-Huy C. “Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health.” Int J Biomed Sci. 2008 Jun;4(2):89-96. PMID: 23675073; PMCID: PMC3614697.[↩]
- Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N. “Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health.” Pharmacogn Rev. 2010 Jul;4(8):118-26. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.70902. PMID: 22228951; PMCID: PMC3249911.[↩]
- Danby FW. “Nutrition and aging skin: sugar and glycation.” Clin Dermatol. 2010 Jul-Aug;28(4):409-11. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2010.03.018. PMID: 20620757.[↩]
- Zheng W, Li H, Go Y, Chan XHF, Huang Q, Wu J. “Research Advances on the Damage Mechanism of Skin Glycation and Related Inhibitors.” Nutrients. 2022 Nov 1;14(21):4588. doi: 10.3390/nu14214588. PMID: 36364850; PMCID: PMC9655929.[↩]
- Swanson D, Block R, Mousa SA. “Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: health benefits throughout life.” Adv Nutr. 2012 Jan;3(1):1-7. doi: 10.3945/an.111.000893. Epub 2012 Jan 5. PMID: 22332096; PMCID: PMC3262608.[↩]
- Spence LA, Henschel B, Li R, Tekwe CD, Thiagarajah K. “Adding Walnuts to the Usual Diet Can Improve Diet Quality in the United States: Diet Modeling Study Based on NHANES 2015-2018.” Nutrients. 2023 Jan 4;15(2):258. doi: 10.3390/nu15020258. PMID: 36678128; PMCID: PMC9865599.[↩]
- Link between hydration and aging. (2023, February 7). National Institutes of Health (NIH).[↩]
- Fuhrman J. “The Hidden Dangers of Fast and Processed Food.” Am J Lifestyle Med. 2018 Apr 3;12(5):375-381. doi: 10.1177/1559827618766483. PMID: 30283262; PMCID: PMC6146358.[↩]
- Cao C, Xiao Z, Wu Y, Ge C. “Diet and Skin Aging-From the Perspective of Food Nutrition.” Nutrients. 2020 Mar 24;12(3):870. doi: 10.3390/nu12030870. PMID: 32213934; PMCID: PMC7146365.[↩]
- Ogata H, Kayaba M, Tanaka Y, Yajima K, Iwayama K, Ando A, Park I, Kiyono K, Omi N, Satoh M, Tokuyama K. “Effect of skipping breakfast for 6 days on energy metabolism and diurnal rhythm of blood glucose in young healthy Japanese males.” Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Jul 1;110(1):41-52. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy346. PMID: 31095288.[↩]
- Kitada M, Ogura Y, Monno I, Koya D. “The impact of dietary protein intake on longevity and metabolic health.” EBioMedicine. 2019 May;43:632-640. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 8. PMID: 30975545; PMCID: PMC6562018.[↩]
- Baum JI, Kim IY, Wolfe RR. “Protein Consumption and the Elderly: What Is the Optimal Level of Intake?” Nutrients. 2016 Jun 8;8(6):359. doi: 10.3390/nu8060359. PMID: 27338461; PMCID: PMC4924200.[↩]
- Spencer RL, Hutchison KE. “Alcohol, aging, and the stress response.” Alcohol Res Health. 1999;23(4):272-83. PMID: 10890824; PMCID: PMC6760387.[↩]
- Goodman GD, Kaufman J, Day D, Weiss R, Kawata AK, Garcia JK, Santangelo S, Gallagher CJ. “Impact of Smoking and Alcohol Use on Facial Aging in Women: Results of a Large Multinational, Multiracial, Cross-sectional Survey.” J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Aug;12(8):28-39. Epub 2019 Aug 1. PMID: 31531169; PMCID: PMC6715121.[↩]
- Flanagan EW, Most J, Mey JT, Redman LM. “Calorie Restriction and Aging in Humans.” Annu Rev Nutr. 2020 Sep 23;40:105-133. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-122319-034601. Epub 2020 Jun 19. PMID: 32559388; PMCID: PMC9042193.[↩]
- Joshi S, Mohan V. “Pros & cons of some popular extreme weight-loss diets.” Indian J Med Res. 2018 Nov;148(5):642-647. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1793_18. PMID: 30666989; PMCID: PMC6366252.[↩]
- Firth J, Gangwisch JE, Borisini A, Wootton RE, Mayer EA. “Food and mood: how do diet and nutrition affect mental wellbeing?” BMJ. 2020 Jun 29;369:m2382. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2382. Erratum in: BMJ. 2020 Nov 9;371:m4269. PMID: 32601102; PMCID: PMC7322666.[↩]
- Redman LM, Ravussin E. “Caloric restriction in humans: impact on physiological, psychological, and behavioral outcomes.” Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Jan 15;14(2):275-87. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3253. Epub 2010 Aug 28. PMID: 20518700; PMCID: PMC3014770.[↩]