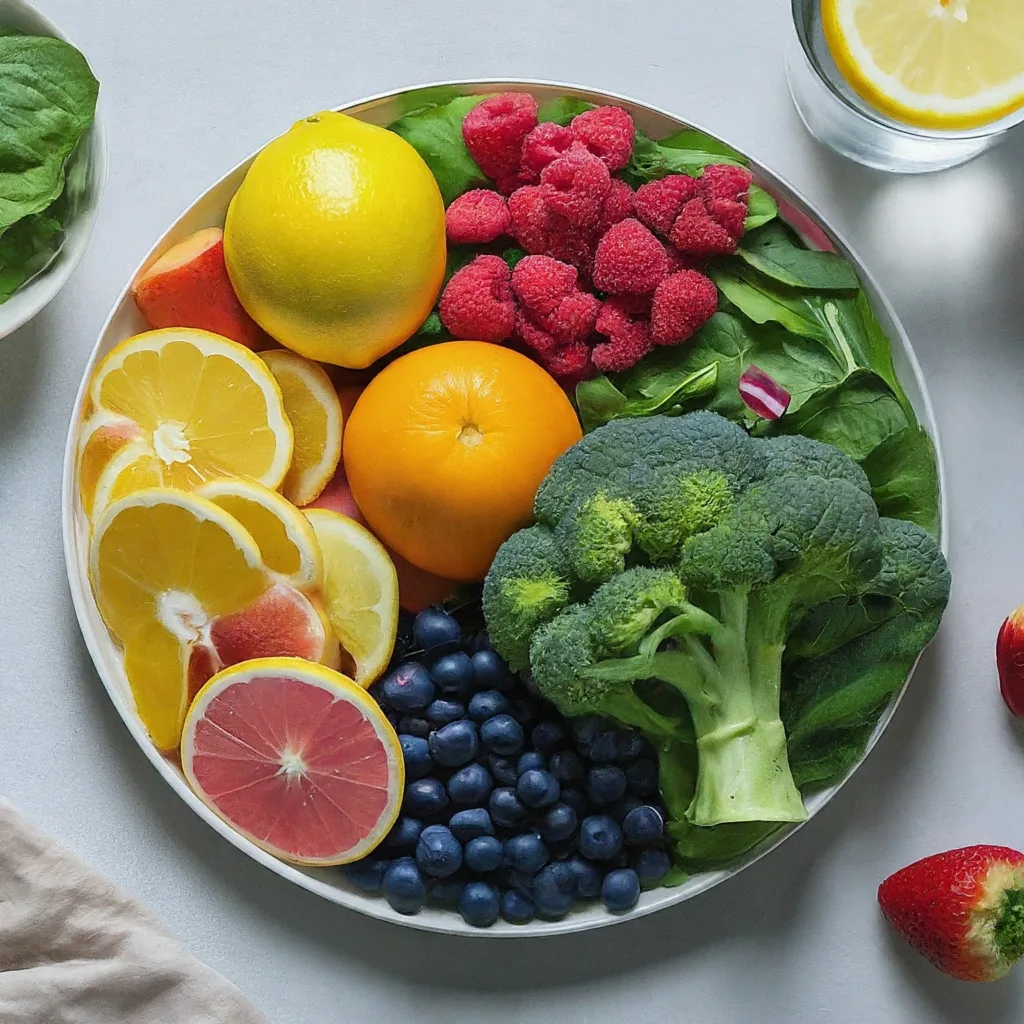
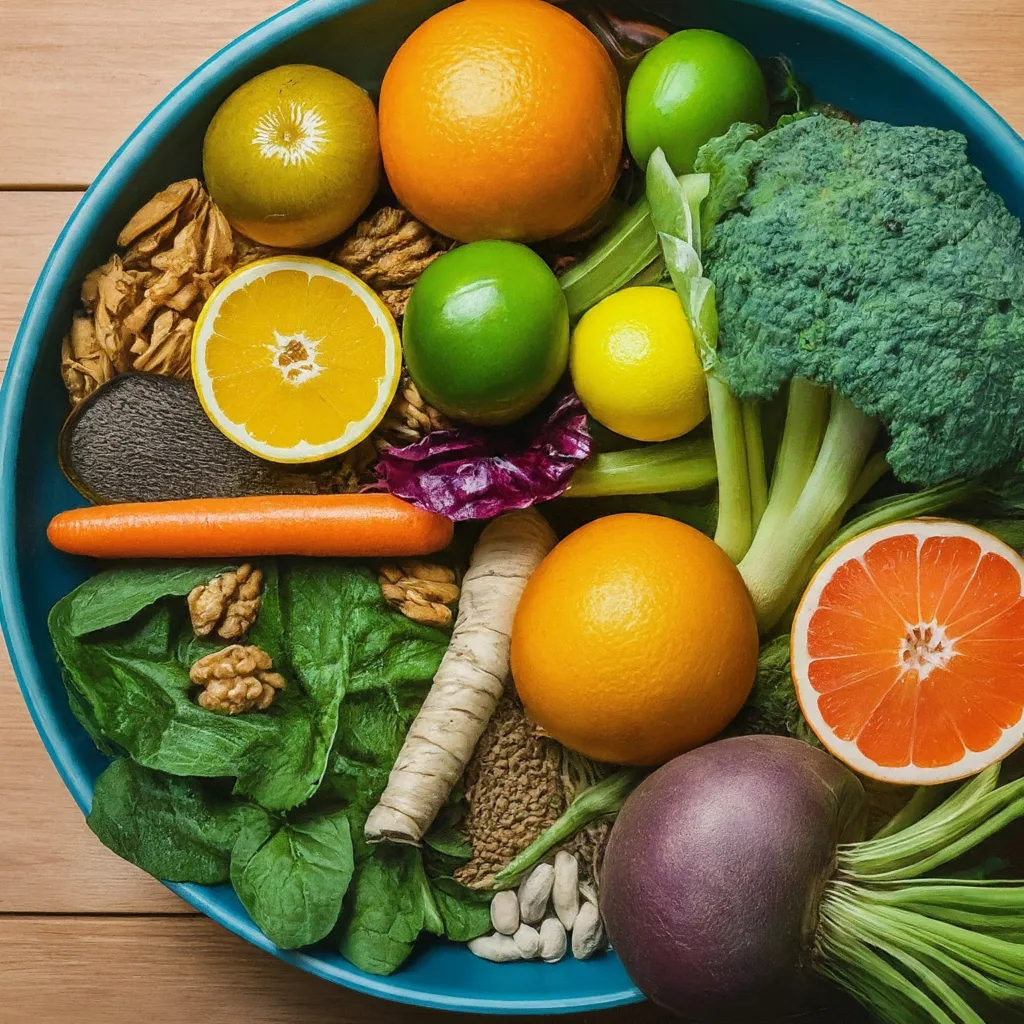
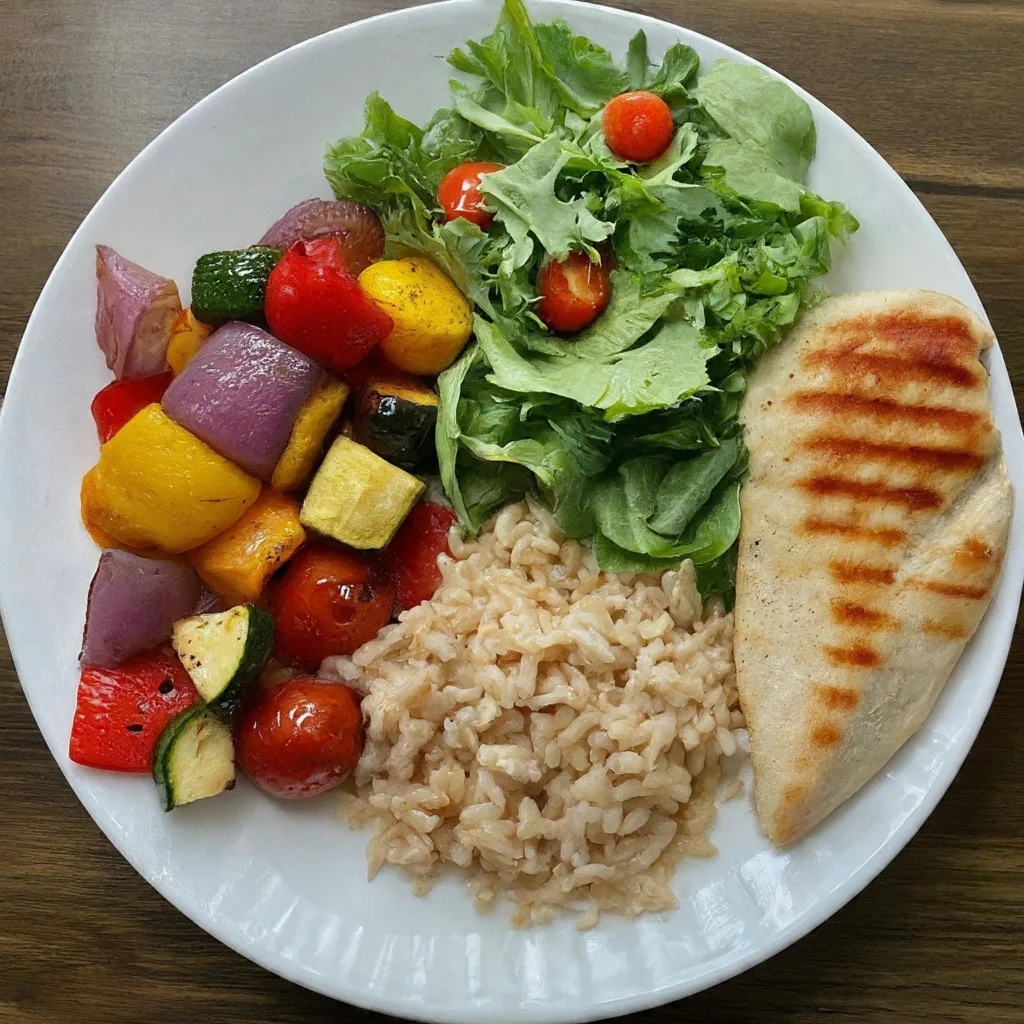
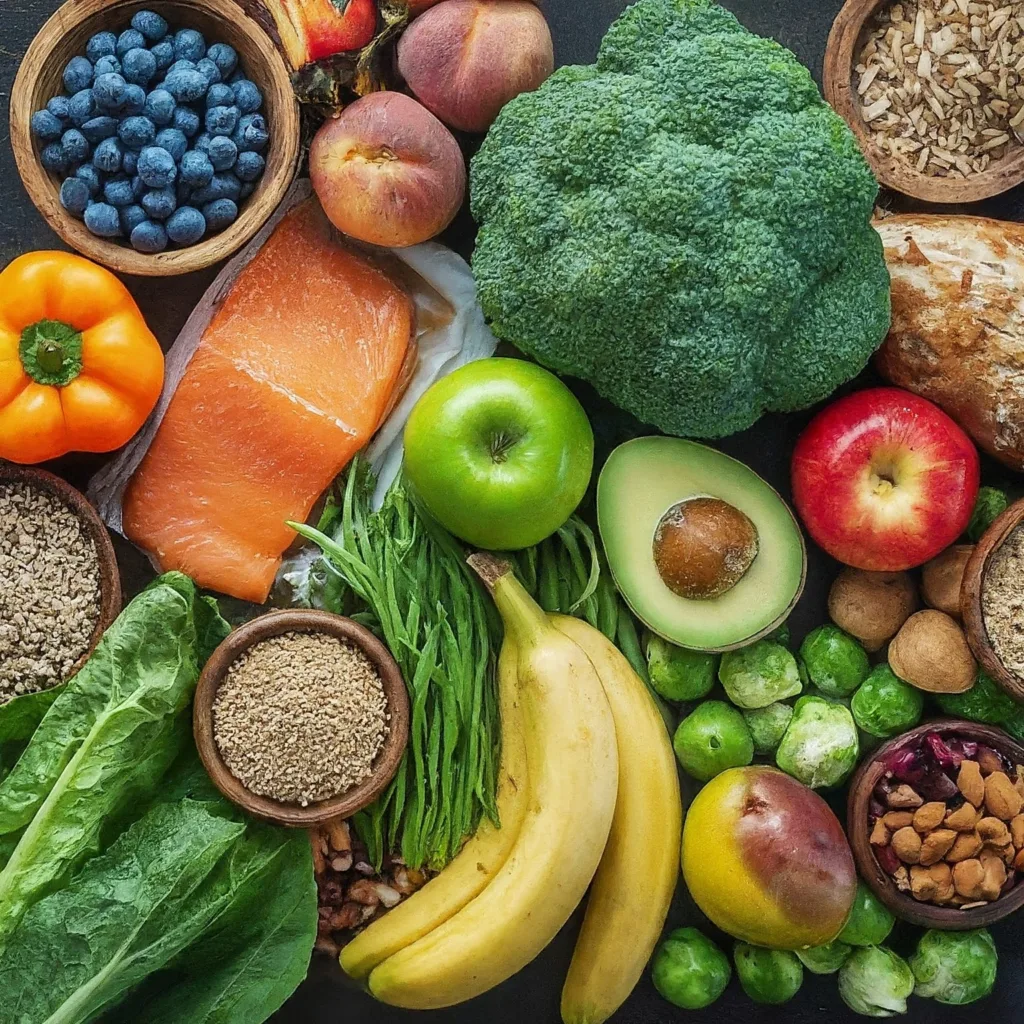
Adopt the “Eat the Rainbow” approach to ensure a diverse and nutrient-rich intake, promoting vitality and wellness through a colorful diet.
This article provides an overview of the “eat the rainbow” concept, exploring its benefits, practical implementation into one’s diet, and strategies for overcoming potential challenges.
In This “Eat the Rainbow And Colorful Diet”
What It Means to “Eat the Rainbow”?
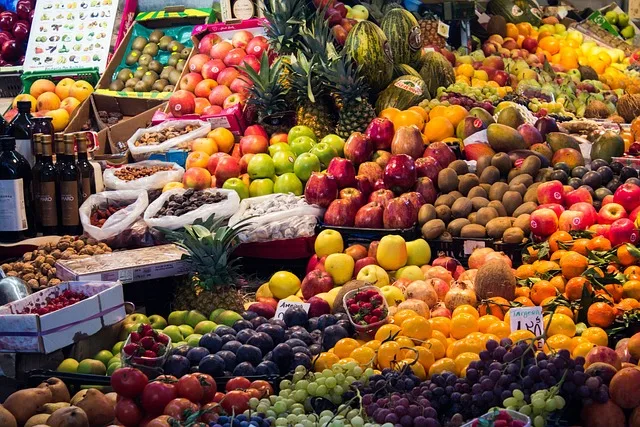

“Eat the Rainbow” is a nutritional guideline that promotes consuming a wide variety of colorful fruits and vegetables regularly. This concept focuses on incorporating foods of different colors into one’s diet to ensure a diverse intake of nutrients and health-promoting compounds.
Individuals can benefit from a broad range of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals by including foods across the spectrum of colors, which are essential for optimal health and well-being. Essentially, “Eat the Rainbow” encourages individuals to diversify their food choices and prioritize colorful fruits and vegetables as a means to enhance overall nutrition and vitality.
Understanding the concept of “Eat the Rainbow”
Health experts frequently encourage individuals to “eat the rainbow” to emphasize the significance of consuming a diverse range of fruits and vegetables. While you may understand the general advice to include colorful produce in your diet, you might question its specific benefits and importance for your health.
Understanding the concept of “Eat the Rainbow” involves acknowledging the value of regularly incorporating a wide variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals.
The Health Benefits of Eating a Colorful Diet

In essence, incorporating the “eat the rainbow” approach into your daily meals means consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables in diverse colors.
Plants derive their vibrant hues from different pigments called phytonutrients, each offering unique nutritional benefits. Research suggests that fruits and vegetables of various colors are associated with higher levels of specific nutrients and health-promoting properties.
While conducting randomized controlled trials to prove the efficacy of phytonutrients poses challenges, population-level studies consistently indicate the advantages of consuming colorful produce for health. By diversifying your diet with a spectrum of colors, you provide your body with an array of essential vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals, supporting overall well-being. 1
Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, such as those with vibrant colors, promote healthy digestion and regularity. They aid in maintaining optimal gut health, preventing constipation, and reducing the risk of digestive disorders.
Certain colorful fruits and vegetables contain compounds that support skin health and appearance. Antioxidants like vitamin C and beta-carotene help combat oxidative stress, promoting youthful-looking skin and a radiant complexion.
Additionally, rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants may help reduce stress, boost energy levels, and support overall mental clarity.
Let’s explore the health benefits associated with different-colored foods, including red, dark red, yellow, orange, green, blue, purple, white, and brown varieties.
Red Foods: Powerhouses of Nutrition
Red fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants and phytonutrients that contribute to their vibrant color and offer numerous health benefits.
- Nutrient-rich foods and veggies: Tomatoes, red bell peppers, strawberries, raspberries, cherries, watermelon, red cabbage, beets
- Main phytonutrients: Lycopene 2, anthocyanins, ellagic acid
- Main vitamins and minerals: Vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium
- Health benefits: Supports heart health, may reduce the risk of certain cancers, promotes skin health, aids in inflammation reduction
Dark Red Foods: Nutrient-Rich Elixirs
Dark red fruits and vegetables derive their deep hues from potent antioxidants and phytochemicals, providing a wealth of nutritional value.
- Nutrient-rich foods and veggies: Red grapes, red onions, cranberries, pomegranates, red apples
- Main phytonutrients: Anthocyanins 3, flavonoids, resveratrol
- Main vitamins and minerals: Vitamin C, vitamin K, manganese
- Health benefits: Supports cardiovascular health, may improve cognitive function, aids in blood sugar regulation, possesses antioxidant properties
Yellow and Orange Foods: Sunshine on Your Plate
Yellow and orange fruits and vegetables boast high levels of beta-carotene and vitamin C, supporting immune function and promoting skin health.
- Nutrient-rich foods and veggies: Carrots, sweet potatoes, oranges, mangoes, apricots, peaches, pineapple
- Main phytonutrients: Beta-carotene 4, zeaxanthin, flavonoids
- Main vitamins and minerals: Vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium
- Health benefits: Promotes eye health, supports immune function, aids in skin health, may reduce the risk of chronic diseases
Green Foods: Nature’s Nutrient-Rich Bounty
Green fruits and vegetables are packed with chlorophyll 5, vitamins, and minerals, offering a multitude of health benefits for overall wellness.
- Nutrient-rich foods and veggies: Spinach, broccoli, kale, green peas, kiwi, green apples, avocados
- Main phytonutrients: Chlorophyll, lutein, zeaxanthin 6
- Main vitamins and minerals: Vitamin K, vitamin C, folate, potassium
- Health benefits: Supports bone health, aids in digestion, may reduce the risk of certain cancers, promotes detoxification
Blue and Purple Foods: Vibrant Health Elixirs
Blue and purple fruits and vegetables contain anthocyanins and flavonoids 7, known for their powerful antioxidant properties and potential health benefits.
- Nutrient-rich foods and veggies: Blueberries, blackberries, eggplant, purple grapes, plums, figs
- Main phytonutrients: Anthocyanins, resveratrol 8, flavonoids
- Main vitamins and minerals: Vitamin C, vitamin K, manganese
- Health benefits: Supports brain health, may improve memory and cognitive function, possesses anti-inflammatory properties, aids in heart health
White and Brown Foods: Often Overlooked but Essential
White and brown fruits and vegetables offer a variety of nutrients such as allicin 9 and quercetin, supporting immune function and heart health.
- Nutrient-rich foods and veggies: Cauliflower, mushrooms, garlic, onions, potatoes, bananas, dates
- Main phytonutrients: Allicin, flavonoids, quercetin 10
- Main vitamins and minerals: Vitamin C, potassium, magnesium
- Health benefits: Supports immune function, aids in digestion, may lower cholesterol levels, promotes heart health
Incorporating Colorful Foods into Your Diet
The benefits of consuming a colorful array of foods is surprisingly straightforward.
To embrace the “eat the rainbow” approach, aim to integrate two to three different-colored fruits or vegetables into every meal, and include at least one in each snack. While it’s not necessary to consume every color daily, strive to include them in your diet several times per week.
The possibilities for incorporating fruits and vegetables into your meals are endless. If fresh produce isn’t readily available year-round in your area, consider adding frozen fruits and vegetables to your meals. They offer the same nutritional benefits, are convenient, and budget-friendly.
Here are some suggestions to infuse your meals with colorful goodness:
Breakfast
- Spinach and tomato omelette with a side of sliced strawberries
- Greek yogurt parfait with layers of blueberries, mango chunks, and kiwi slices
- Oatmeal topped with sliced bananas, raspberries, and a drizzle of honey
Lunch
- Mixed green salad with sliced carrots, bell peppers, and grilled chicken
- Quinoa salad with roasted sweet potatoes, avocado slices, and cherry tomatoes
- Veggie wrap filled with hummus, cucumber, shredded purple cabbage, and spinach leaves
Dinner
- Grilled salmon served with roasted asparagus and mashed sweet potatoes
- Stir-fried tofu with broccoli, bell peppers, and mushrooms served over brown rice
- Spaghetti squash topped with marinara sauce, sautéed spinach, and grated Parmesan cheese
Snacks
- Apple slices with almond butter
- Celery sticks with hummus
- Carrot and cucumber sticks with Greek yogurt dip
- Blueberry and raspberry smoothie
- Trail mix with mixed nuts, dried cranberries, and dark chocolate chips
Bottom line
Potential Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Addressing picky eating habits can often pose a significant challenge, particularly when trying to introduce new and unfamiliar foods into one’s diet. However, there are several effective strategies that can help overcome these hurdles.
Addressing picky eating habits
One such approach involves actively involving picky eaters in the meal planning and preparation process. By allowing them to participate in selecting ingredients and assisting with cooking, individuals may feel more invested in their food choices and more inclined to try new foods.
Furthermore, offering a diverse range of options and experimenting with various cooking methods can help expand the palate of picky eaters. For example, presenting fruits and vegetables in different forms such as raw, roasted, or blended into smoothies can make them more appealing and enjoyable.
Additionally, incorporating familiar foods alongside new additions can help ease the transition and make trying new foods feel less daunting.
Dealing with food allergies or intolerances
When it comes to dealing with food allergies or intolerances, careful attention to ingredient labels and alternative food options is essential. Individuals with food allergies or intolerances must be diligent in reading labels to identify potential allergens and avoid cross-contamination. It may also be beneficial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who can provide personalized recommendations and support tailored to specific dietary needs.
Budget-friendly options for eating the rainbow
In terms of budget-friendly options for eating the rainbow, there are several strategies that can help individuals make nutritious food choices without breaking the bank. One approach is to prioritize seasonal produce, as fruits and vegetables that are in season are often more affordable and readily available. Additionally, buying in bulk and taking advantage of sales and discounts can help stretch your grocery budget further. For those on a tight budget, opting for frozen or canned fruits and vegetables can be a cost-effective way to incorporate a variety of colorful foods into meals.
Bottom line
Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting the “Eat the Rainbow” approach offers a multitude of health benefits. By incorporating a diverse array of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet, you provide your body with essential nutrients and antioxidants that support overall health. From boosting immune function to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, the vibrant hues of these foods signify a wealth of nutritional value.
Therefore, it’s essential to prioritize colorful foods for optimal health and vitality. Embracing the spectrum of colors in your diet not only adds visual appeal to your meals but also ensures that you’re nourishing your body with a variety of vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals. So, make it a priority to include a rainbow of fruits and vegetables in your daily meals to reap the numerous health benefits they offer.
- Wallace TC, Bailey RL, Blumberg JB, Burton-Freeman B, Chen CO, Crowe-White KM, Drewnowski A, Hooshmand S, Johnson E, Lewis R, Murray R, Shapses SA, Wang DD. “Fruits, vegetables, and health: A comprehensive narrative, umbrella review of the science and recommendations for enhanced public policy to improve intake.” Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(13):2174-2211. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1632258. Epub 2019 Jul 3. PMID: 31267783.[↩]
- Mozos I, Stoian D, Caraba A, Malainer C, Horbańczuk JO, Atanasov AG. “Lycopene and Vascular Health.” Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 23;9:521. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00521. PMID: 29875663; PMCID: PMC5974099.[↩]
- Khoo HE, Azlan A, Tang ST, Lim SM. “Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits.” Food Nutr Res. 2017 Aug 13;61(1):1361779. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1361779. PMID: 28970777; PMCID: PMC5613902.[↩]
- Grune T, Lietz G, Palou A, Ross AC, Stahl W, Tang G, Thurnham D, Yin SA, Biesalski HK. “Beta-carotene is an important vitamin A source for humans.” J Nutr. 2010 Dec;140(12):2268S-2285S. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.119024. Epub 2010 Oct 27. PMID: 20980645; PMCID: PMC3139236.[↩]
- Martins T, Barros AN, Rosa E, Antunes L. “Enhancing Health Benefits through Chlorophylls and Chlorophyll-Rich Agro-Food: A Comprehensive Review.” Molecules. 2023 Jul 11;28(14):5344. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145344. PMID: 37513218; PMCID: PMC10384064.[↩]
- Murillo AG, Hu S, Fernandez ML. “Zeaxanthin: Metabolism, Properties, and Antioxidant Protection of Eyes, Heart, Liver, and Skin.” Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Sep 11;8(9):390. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090390. PMID: 31514298; PMCID: PMC6770730.[↩]
- Ullah A, Munir S, Badshah SL, Khan N, Ghani L, Poulson BG, Emwas AH, Jaremko M. “Important Flavonoids and Their Role as a Therapeutic Agent.” Molecules. 2020 Nov 11;25(22):5243. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225243. PMID: 33187049; PMCID: PMC7697716.[↩]
- Salehi B, Mishra AP, Nigam M, Sener B, Kilic M, Sharifi-Rad M, Fokou PVT, Martins N, Sharifi-Rad J. “Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits.” Biomedicines. 2018 Sep 9;6(3):91. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6030091. PMID: 30205595; PMCID: PMC6164842.[↩]
- Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC, Nwachukwu ID, Slusarenko AJ. “Allicin: chemistry and biological properties.” Molecules. 2014 Aug 19;19(8):12591-618. doi: 10.3390/molecules190812591. PMID: 25153873; PMCID: PMC6271412.[↩]
- Anand David AV, Arulmoli R, Parasuraman S. “Overviews of Biological Importance of Quercetin: A Bioactive Flavonoid.” Pharmacogn Rev. 2016 Jul-Dec;10(20):84-89. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.194044. PMID: 28082789; PMCID: PMC5214562.[↩]